Refurbished engines
General overhauled engines / engine revision
First of all, to be clear about the definition of the term:
All wearing parts are renewed here or revised accordingly. The mileage is seto 0 km and the function and condition equivalent to a new engine. It is less expensive than a new engine - specific problems are improved, e.g. through the use of reinforced components. Significant increase in value of the vehicle Conclusion: Highest quality and yet cheaper as a new engine. Recommended for engines with high mileage and if you want to drive the car for a long time without incident. Recommended for engines with known weak points or design errors (e.g. VW T5).
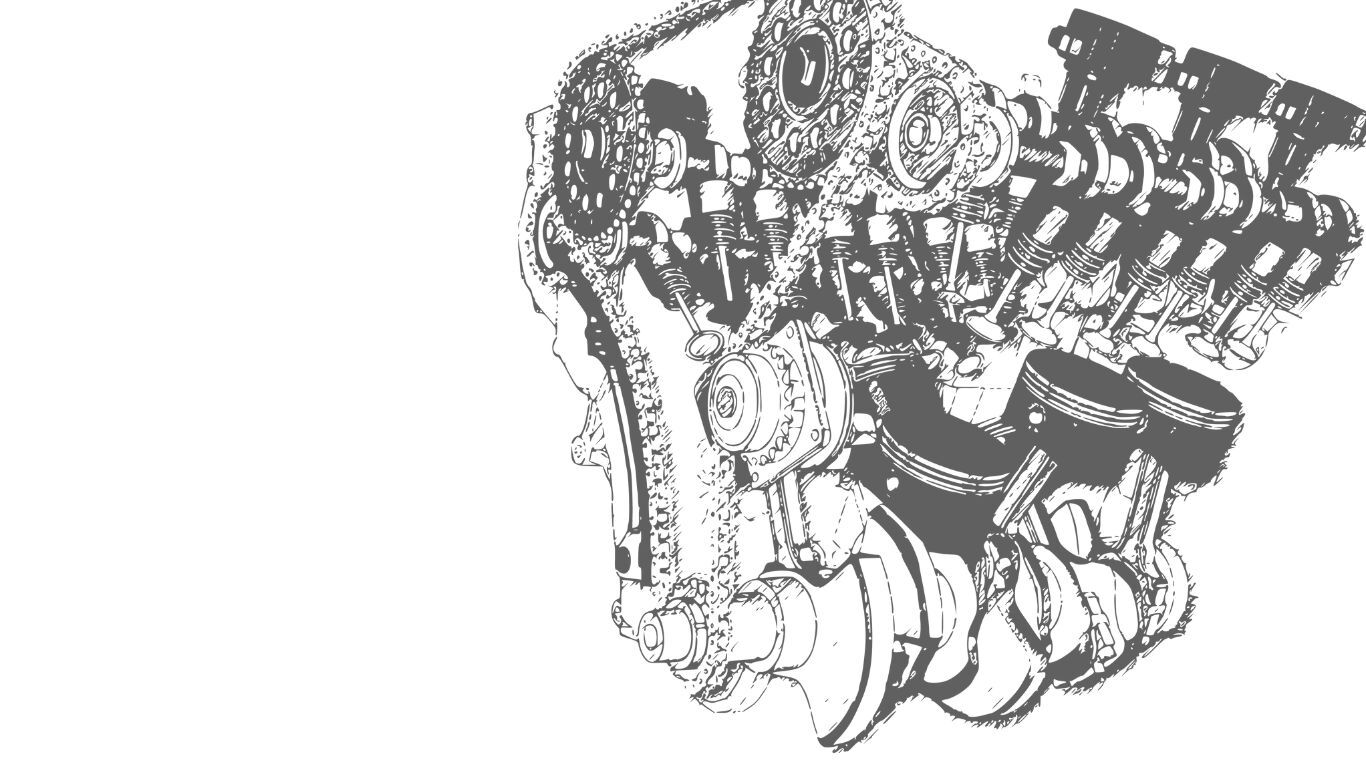
During the general overhaul, the entire engine is then completely dismantled and then completely rebuilt.
Engine repairs / partial overhauls, where only the damage is repaired, must be clearly distinguished from this!
That's why you often find offers on the Internet for engines that have been completely overhauled, but which have mostly been overhauled or where only the damage has been repaired, or in very bad cases, the engine supplied has been repainted but nobody has even looked at the inside.
With us you get overhauled engines, exact work done on the engine type in question can be requested, here is a general listing
These motors are usually not stock items and are made to order, ie an additional processing time of 4-8 working days is to be expected (depending on the motor type). More details on request. It is necessary to return the old part, if this occurs later, a deposit for the old part of usually 500 € (amount appears in the invoice) must be paid at the latest on delivery.
The work steps that lead to a completely overhauled engine are not uniformly regulated. Therefore, in principle, anyone can call an engine overhauled, even if the scope of repairs was very small.
Steps: General overhaul / engine revision
A complete overhaul requires an intact, crack-free engine block. The following work steps are necessary here:
- Remove the engine and completely disassemble it (sometimes special tools are required), under certain circumstances drill out the engine block to the next piston size, obtain new oversize pistons, check the oil system (pump, pressure valves if necessary) and replace them if necessary, check the crankshaft bearings, grind the crankshaft and oversize if necessary -Install bearings, check connecting rod bearings, possibly re-store the connecting rods, replace the cylinder head, or rework if necessary, new valves, new guides and new hydraulic tappets, check the condition of the camshafts, replace if necessary, check the camshaft bearings, possibly replace the bearing bushes, everything with new seals ( Gasket set) assemble, adjust, check, where necessary with new stretch bolts (connecting rod, cylinder head) for engines with a timing chain, this is also replaced. Engine reseal Engine cleaning and painting
Known design flaws:
BMW: N46 B20 (z.B. BMW E87 120i)
This type of damage is well known: piston tilting, skipping timing chains and connecting rod bearing damage. This is how you recognize the damage: Loud rattling when accelerating, reading error codes, increased oil consumption and the engine suddenly stalling and no longer being able to start.
Audi: EA888 BZB (zB Audi A3 8P 1.8 TFSI)
This type of damage is well known: Defective piston rings or misaligned control times due to defective camshaft setting wheels. How to recognize the damage: compression test. Read error codes or increased oil consumption.
VW: EA 189 CFCA (eg VW T5 2.0 TDI 132 kW)
This damage is well known: high oil consumption (up to four liters per 1000 km), clogged injectors. The damage is caused by loose aluminum particles from the EGR cooler, which get into the combustion chambers and damage cylinder surfaces and piston bridges there. How to recognize the damage: compression test, checking the running surfaces with an endoscope (150 to 300 euros).


